Verilog 공부
HDLBits (Verilog Language - Procedures) - Verilog 문제 풀이 1-4
Opens
2024. 9. 6. 12:43
https://github.com/dlwotjr/HDL_Bits
GitHub - dlwotjr/HDL_Bits
Contribute to dlwotjr/HDL_Bits development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
https://hdlbits.01xz.net/wiki/Main_Page
HDLBits
HDLBits — Verilog Practice HDLBits is a collection of small circuit design exercises for practicing digital hardware design using Verilog Hardware Description Language (HDL). Earlier problems follow a tutorial style, while later problems will increasingl
hdlbits.01xz.net
- Verilog의 조건문에는 if, else, repeat, while, for, case가 있음
begin / end
- c의 함수에서 {}와 같은 의미
- 대부분 initial always forever if-else와 함께 사용
initial
- 최초의 시작시점
- 시뮬레이션의 시작 시점 - 0ns
always
- @ : sensitive list 이후 나오는 변수들이 변화에 따라 움직임
- 보통 always사용해 플립플롭을 모델링함(상승에지 posegde/ 하강 에지-negedge)
fork - join
- 개별 process의 생성 및 수행
- join문에서 모든 process가 종료되면 서브루틴이 종료됨
- process를 parallel하게 수행
if-else
- case의 표현식에 전체 bit를 사용할 수 있는게 아니면 if-else쓰는게 좋음
example : 4:1 MUX
always @(*)
begin
if(sel == 'h0)
out = a;
else if(sel == 'h1)
out = b;
else if(sel == 'h2)
out = c;
else if(sel == 'h3)
out = d;
endcase statement
- 초기값이나 defualt없으면 회로 합성시에 latch 발생시킴
example : 4:1 MUX
always @(*)
begin
case(sel)
0 : out = a;
1 : out = b;
2 : out = c;
3 : out = d;
default : out = 'bx;
endcase
endTernary Operator
- 삼항연산자 - 근데 연쇄도 가능함
result = (expression) ? expression_a : expression_b;
example : 4:1 MUX
assign out = (sel == 0) ? a :
(sel == 1) ? b :
(sel == 2) ? c : d;for statement
for( init_expression; cond_expression; loop_expression ) begin
statements;
endwhile statement
while ( cond_expression ) begin
statements;
end
문제 : always Blocks(combinational)
- combinational always Blocks == assign statements (두개로 표현가능)
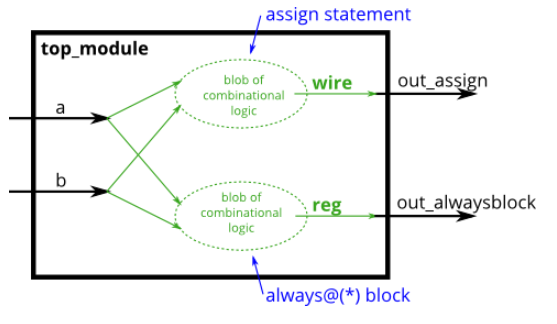
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_alwaysblock
);
assign out_assign = a & b;
always @(*) out_alwaysblock = a & b;
endmodule
문제 : Always Block(clocked)
verilog 의 할당 3가지 방식
- 연속 할당(Continuous Assignment) / 차단 할당(Blocking Assignment) / 비차단 할당(Non-Blocking Assignment)
- Continuous Assignment
- assign a= b+c;
- 조합회로에서 사용
- assign이 몇개든 순서에 상관없이 할당됨
- Blocking Assignment
- always @($*$) a= b+c;
- 이걸 할당하는 동안 밑에 있는 것은 순서를 기다리며 할당이 되지 않음
- 내부 값이 바뀌면 순차적으로 할당을 함
- Non-Blocking Assignment
- always @(posedge clk) a<=b+c;
- clk의 rising edge에서만 assign됨
- <= 로 할당함
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input clk,
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always_comb,
output reg out_always_ff );
assign out_assign = a ^ b;
always @(*) out_always_comb = a ^b;
always @(posedge clk) out_always_ff <= a^b;
endmodule
문제 : if statement
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
input sel_b1,
input sel_b2,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always );
assign out_assign = sel_b1&sel_b2 ? b : a;
always @(*) begin
if(sel_b1==1 && sel_b2 ==1)
out_always = b;
else
out_always = a;
end
endmodule
문제 : if statement latches
- "출력을 변경하지 않고 유지"라는 동작은 상태 기억이 필요 -> latch 생성
- else 항상 쓸 것 of default값
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module (
input cpu_overheated,
output reg shut_off_computer,
input arrived,
input gas_tank_empty,
output reg keep_driving ); //
always @(*) begin
if (cpu_overheated)
shut_off_computer = 1;
else
shut_off_computer = 0;
end
always @(*) begin
if (~arrived)
keep_driving = ~gas_tank_empty;
else
keep_driving = ~arrived;
end
endmodule
문제 : Case statement
module top_module (
input [2:0] sel,
input [3:0] data0,
input [3:0] data1,
input [3:0] data2,
input [3:0] data3,
input [3:0] data4,
input [3:0] data5,
output reg [3:0] out );//
always@(*)
begin // This is a combinational circuit
case(sel)
3'b000 : out = data0;
3'b001 : out = data1;
3'b010 : out = data2;
3'b011 : out = data3;
3'b100 : out = data4;
3'b101 : out = data5;
default : out = 3'b000;
endcase
end
endmodule
문제 : Priority Encoder
- 나는 Don't care term을 이용해 문제를 품
- casez라는 것을 이용하면 가능
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos );
always@(*)begin
casez(in)
4'b???1 : pos = 2'd0;
4'b??10 : pos = 2'd1;
4'b?100 : pos = 2'd2;
4'b1000 : pos = 2'd3;
default pos = 2'd0;
endcase
end
endmodule- 문제에서 제시한 답안
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos
);
always @(*) begin // Combinational always block
case (in)
4'h0: pos = 2'h0; // I like hexadecimal because it saves typing.
4'h1: pos = 2'h0;
4'h2: pos = 2'h1;
4'h3: pos = 2'h0;
4'h4: pos = 2'h2;
4'h5: pos = 2'h0;
4'h6: pos = 2'h1;
4'h7: pos = 2'h0;
4'h8: pos = 2'h3;
4'h9: pos = 2'h0;
4'ha: pos = 2'h1;
4'hb: pos = 2'h0;
4'hc: pos = 2'h2;
4'hd: pos = 2'h0;
4'he: pos = 2'h1;
4'hf: pos = 2'h0;
default: pos = 2'b0; // Default case is not strictly necessary because all 16 combinations are covered.
endcase
end
// There is an easier way to code this. See the next problem (always_casez).
endmodule- if문으로 푼다면?
module priority_encoder_4bit (
input [3:0] in, // 4-bit input
output reg [1:0] out // 2-bit output
);
always @(*) begin
if (in[3])
out = 2'b11; // If bit 3 is 1, output is 3
else if (in[2])
out = 2'b10; // If bit 2 is 1, output is 2
else if (in[1])
out = 2'b01; // If bit 1 is 1, output is 1
else if (in[0])
out = 2'b00; // If bit 0 is 1, output is 0
else
out = 2'b00; // If none of the bits are 1, output is 0
end
endmodule
문제 : Priority Encoder with casez
- casez -> z는 dont care term 나타내는 자료형!
- ?도 가능은 하지만 z로 명시적 표현하자!
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output reg [2:0] pos );
always@(*)begin
casez(in)
8'bzzzzzzz1 : pos = 3'd0;
8'b??????10 : pos = 3'd1;
8'b?????100 : pos = 3'd2;
8'b????1000 : pos = 3'd3;
8'b???10000 : pos = 3'd4;
8'b??100000 : pos = 3'd5;
8'b?1000000 : pos = 3'd6;
8'b10000000 : pos = 3'd7;
default pos = 3'd0;
endcase
end
endmodule
문제 : avoiding latch
- 여러개를 조절하려면? - begin / end
module top_module (
input [15:0] scancode,
output reg left,
output reg down,
output reg right,
output reg up );
always @(*) begin
up = 1'b0; down = 1'b0; left = 1'b0; right = 1'b0;
case (scancode)
16'he06b : left = 1;
16'he072 : down = 1;
16'he074 : right = 1;
16'he075 : up = 1;
default :begin up = 0; down =0; left =0; right =0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule